An Underground Kingdom

Scaly Hedgehog mushrooms, Sarcodon imbricatus, found in coniferous woods in the district of Eggingen in the city of Ulm in southern Germany. Photo by H. Krisp.
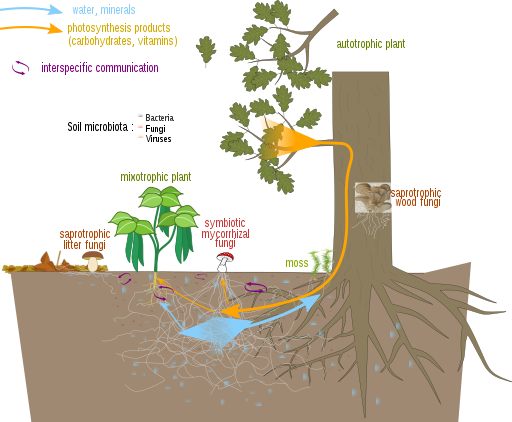
Mycorrhizal fungi are in a symbiotic relationship with autotrophic plants. The relationship is usually mutually beneficial, the fungus providing the plant with water and minerals from the soil and the plant providing the fungus with photosynthesis products. Some fungi are parasitic, however, taking from plants without providing benefits. Conversely, some mixotrophic plants connect with mycorrhizal fungi to obtain photosynthesis products from other plants. Finally, saprotrophic fungi live on dead organic matter without establishing a symbiosis with plants. Illustration and explanation by Charlotte Roy and Salsero35.
“The Wood Wide Web”, a segment of the PBS NOVA web series Gross Science, produced and presented by Anna Rothschild.
Are the trees sentient? Are mushrooms aware of their part in the bigger picture during their brief look around above ground before they produce spores and collapse back into the fecund earth? Of course not. But assemble all the parts, adding pieces as in a jigsaw puzzle, and it does indeed seem the Earth itself is a living thing called Gaia. This awareness, lost to us for centuries, is now returning dimly, though it was always there for those prepared to observe carefully the natural world, such as how a plant wrenched from its native soil and potted with great attention to its needs still rarely thrived as it would have had it been allowed to stay at home. The newly potted plant receives all it requires in water and mineral nutrients; yet in isolating the plant from its underground social network can it be said, perhaps only fancifully, to be lonely?
— Izzy 






