You Don’t Have to Do This

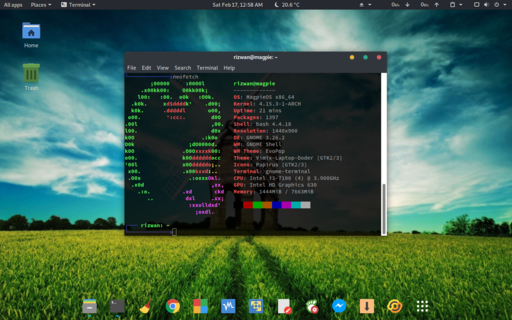
U.S. Representative Ilhan Omar (D-MN) speaking in December 2018 to about 200 workers protesting conditions at an Amazon workplace in Shakopee, Minnesota. Photo by Fibonacci Blue. Protests by workers in this country against unfair labor practices by giant companies like Amazon would get a slingshot-like boost if lawmakers would repeal the anti-union legislation passed in the last 50 years at the behest of corporations.
Some people simply won’t care, of course, and will remain interested only in what’s easiest and most convenient for them. This is not for them. Others who are concerned about voting with their dollars, however, should know there are ways to find alternatives to signing on with the big technology companies, and that informing themselves doesn’t have to suck up an inordinate amount of their time and energy. Currently there is almost no labeling on technology products and services such as there is on food for sale in supermarkets, informing consumers of organic and non-GMO options, and of nutritional content. There should be similarly easily apparent labels for technology, listing ratings from an impartial source, if such is possible, on a company’s treatment of workers, suppliers, and the environment. The companies are now required by law to enumerate the ways they use customer information, but that is for the most part buried in fine print legalese that few consumers bother to read.
In episode #1938, “Theresa Syndrome”, from the radio show Car Talk, the portion of the show relevant to this post starts at the 10:45 mark with a call from Brian in Harrisonville, Kentucky. Questions of ethics come up every day in everyone’s lives, and in this case as in many others, arguments of efficiency that mask motives of self-interest are all too common.
Until the technology industry catches up with at least the halting steps the food industry has taken to inform consumers about what they are buying and what kind of ethical or unethical behavior they in turn support with their purchases, it will remain up to individual consumers to inform themselves. Globalization has made it easy to hide the ugly details of technology manufacturing halfway around the world. Out of sight, out of mind. It’s not as if things were far better 100 years ago, though, because at that time for most Americans a sweatshop on New York City’s Lower East Side was as much on the other side of the world as a sweatshop in Bangladesh is today. Speed of travel and communications have changed the seeming size of the world, but sadly not the willingness of businesses and governments to exploit the less fortunate, and of the more fortunate to turn a blind eye.
— Techly 
Editor’s note: Bonus points to readers who note advertising on this site for the products of one of the companies criticized in this post. It’s hard, maybe impossible, to exist in the modern world without some compromises, and like everybody else, writers have to eat. With a little effort and attentiveness, people do what they can to make the world a better place, but no one is without faults, and as Joe E. Brown said at the end of the movie Some Like It Hot, “Well, nobody’s perfect.”