Legal judgments in lawsuits against the makers of Roundup herbicide continue accumulating in the plaintiffs’ favor, with
the latest one entailing an award of $2.05 billion to a married couple who alleged that they each contracted
non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) from years of using the herbicide in their home garden. As in many lawsuits, high dollar amounts are likely to come down a great deal in the final settlement, and most of the money will end up in the hands of lawyers, not the plaintiffs.
Glyphosate is the active ingredient in Roundup and similar generic herbicides, and it is glyphosate which the plaintiffs in thousands of lawsuits around the country are alleging is linked to their cancer. Meanwhile, glyphosate continues to be readily available without label warnings to home gardeners as well as professional landscapers and farmers since the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has not ruled it is a carcinogen. European environmental and health organizations have ruled glyphosate is a probable carcinogen, differing from their American counterparts because they reviewed independent scientific studies instead of regulatory studies, many of them funded by agribusiness.
 Welted thistle (
Welted thistle (Carduus crispus
) possesses some fine qualities, including pretty flowers as seen here, but most people consider it a weed. Photo by dae jeung kim.While United States government agencies continue to tilt the scales in favor of agribusiness, the courts appear to have no such bias. Consumers in that case have little recourse other than to seek compensation through the courts for their pain and suffering, which they allege were caused by the makers of Roundup (first Monsanto, and currently Bayer) and other purveyors of glyphosate herbicides. Consumers who are still healthy and use herbicides might want to exercise caution by looking for other options, though the only way they would know that is through their own research or by word of mouth, since there continue to be no cautionary statements about the risk of cancer on the label of glyphosate products the way there are for instance on cigarette packs.
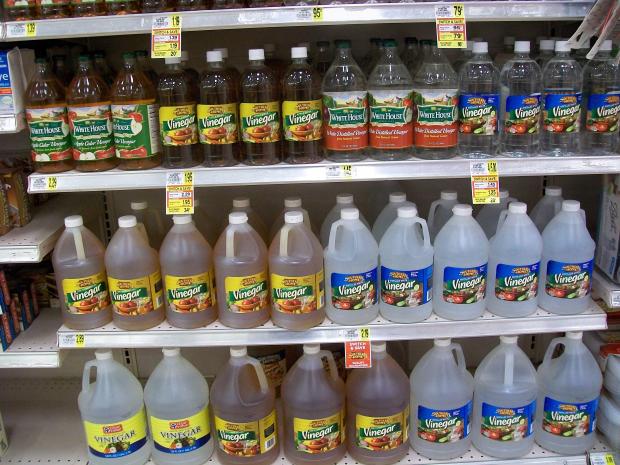 Bottles of vinegar at a supermarket. Safer to use than horticultural vinegar, this more easily available common household vinegar may be a better option for casual users who do not require a heavy duty herbicide. Photo by Ms angie gray.
Bottles of vinegar at a supermarket. Safer to use than horticultural vinegar, this more easily available common household vinegar may be a better option for casual users who do not require a heavy duty herbicide. Photo by Ms angie gray.
A safer herbicide option is vinegar. Ancient cultures derived vinegar from soured grape wine, but since it can be made from
anything that produces ethanol, today most of it is sourced from corn, a cheap source. Unlike glyphosate, which migrates to the roots of affected plants, vinegar only burns the tops, meaning gardeners will have to reapply it when the weed sprouts new growth. Also unlike glyphosate, vinegar does not damage soil fertility with long term use. Damage to soil fertility is another effect of glyphosate that the manufacturers dispute even though
some scientific researchers have upheld the observations of the effect by attentive farmers and gardeners.
Gardeners will be disappointed in
the weak effect of using the vinegar commonly sold in grocery or home improvement stores, and that is because it is only a 5 to 7 percent solution of acetic acid in water meant for pickling food or
cleaning surfaces, not killing weeds. For home gardeners,
the most effective vinegar for killing weeds that is appropriately labeled as such, with accompanying safety warnings, is 20 to 30 percent acetic acid. Probably by reason of the low popularity of strong vinegar and the danger for casual users in believing it is relatively harmless, it appears to be available online only, not in stores. Vinegar that strong, while still mostly water, is
potently acrid stuff which can burn a user’s mucous membranes, eyes, and skin, and may corrode hard surfaces and harm any small animals, such as toads, living in a garden. Test a small area first if there’s a chance overspray could affect something like bricks in a walkway. The best that can be said is it’s a good thing weeds are outside in the open air. Spraying strong vinegar in the garden may be unpleasant for the applicator and those in the vicinity and should be done with caution, but unlike using glyphosate, there’s less risk of serious damage to the gardener and the garden.
— Izzy