Through a Glass Darkly
12 For now we see through a glass, darkly; but then face to face: now I know in part; but then shall I know even as also I am known.
13 And now abideth faith, hope, charity, these three; but the greatest of these is charity.”
— The Apostle Paul in a letter to the Corinthians, 1 Corinthians 13:11-13, from the King James Version of the Bible.
DNA kits are very popular now, both for people ordering them for themselves and for those giving them as gifts. Sales of kits doubled in 2017 over all previous years, and have increased again in 2018 over 2017. Interest appears to derive mostly from curiosity about immediate ancestors, on which the kits do a good job of enlightening people, and secondarily about genetic health risks, on which the kits dealing with the subject deliver mixed results, needing confirmation from a medical professional.

Portraits of six generations of the Sternberg family in Jiří Sternberg’s study, Český Šternberk Castle, Czech Republic. Photo by takato marui. Tracing ancestry is easier in the pure bred lines and close quarters of Old Europe than in the melange of ethnicities and transcontinental migrations of the New World.
It is interesting, however, that DNA test results for black people yield an average of 25 percent European ancestry. It is not surprising there has been mixing of the races, despite laws against miscegenation going back centuries, but that black people have a much higher percentage of European ancestry than white people have a percentage of African ancestry, and yet black people are still and always considered black. This is Pudd’nhead Wilson territory, in which even a tiny percentage of African blood is tantamount to an entirely African genetic heritage. In America, once a person has been accepted into white society, it requires a considerable amount of African genetic input, along with other factors involving economics and relationships, for a person to fall from grace, as it were, from whiteness to blackness.
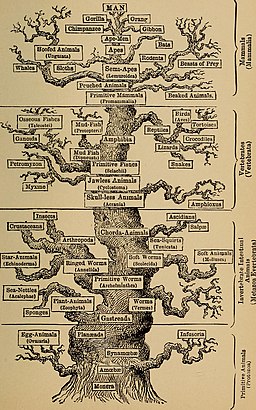
In this 1896 illustration by Ernst Haeckel (1834-1919), “Man” is precariously at the top of a tree encompassing all life on earth.
The immigration scene of young Vito Corleone, played by Oreste Baldini, in Francis Ford Coppola’s 1974 film The Godfather: Part II. Unlike Vito Corleone when he matured, the majority of immigrants, then as now, do not end up engaged in dangerous and unlawful activities, despite what rabble rousing politicians want everyone to believe.
There also appears to be an assumption among even open-minded white people that since Africa is the cradle of all humanity, then Africans themselves must be genetically closer to that cradle than the rest who emigrated to far continents. African ancestry noted in the DNA test results must, they reason, be hearkening back to long ago ancestors white people share with everyone on earth. No. The test results show genetic input from recent African ancestors. And those recent African ancestors have evolved along with everyone else on earth, including Europeans, triggered by similar environmental and social changes pushing them to adapt. The European discoverers should not be so quick to flatter themselves with ideas of inherent superiority that they lose sight of how other societies have adapted quite well under unique circumstances without prizing discovery and conquest above all else as the sine qua non of human existence.
— Ed.