Without Due Process of Law
― from The Federalist Papers, No. 51, by James Madison.
United States Attorney General Jeff Sessions is a fan of civil asset forfeiture, and last year he reinstated the federal partnership with state and local authorities that had been ended by the previous Attorney General, Eric Holder. That partnership allows state and local police to share seized assets with federal authorities if they claim even the flimsiest trespass on federal law by the forfeited assets (in a pretzel-like twist of legal reasoning, it is the assets themselves that are accused, not the person or persons who own them). Engaging the federal government in this way allows state and local police to bypass their civil asset forfeiture laws because they are superseded by federal laws, which are often more favorable to the police. The feds then give the state and local cops a kickback of all or part of the proceeds. This is called “equitable sharing” or, more cutely, “federal adoption”.

Getting pulled over for a minor traffic violation while carrying a large amount of cash can lead to a nightmare civil asset forfeiture scenario for the driver, regardless of the legitimacy of his or her claim to the cash. Only the rich can afford to fight city hall in court. Photo by photoo.uk.
No person shall be held to answer for a capital, or otherwise infamous crime, unless on a presentment or indictment of a Grand Jury, except in cases arising in the land or naval forces, or in the Militia, when in actual service in time of War or public danger; nor shall any person be subject for the same offence to be twice put in jeopardy of life or limb; nor shall be compelled in any criminal case to be a witness against himself, nor be deprived of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor shall private property be taken for public use, without just compensation.
― The Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, with the due process clause.
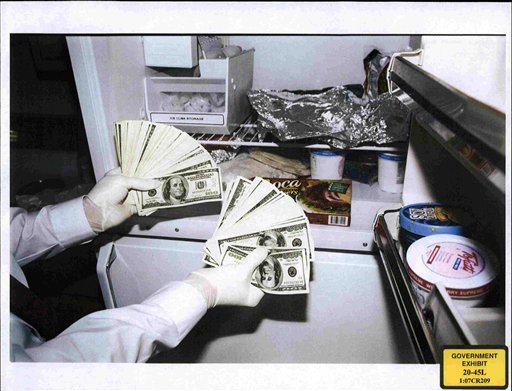
Cash found in a freezer at the Washington, D.C. home of Congressman William J. Jefferson of Louisiana. This photo was entered as evidence in July 2009 showing what was seized in August 2005 from the freezer of the home of then Rep. William Jefferson, D-New Orleans. Jurors in the trial of Jefferson, who lost his re-election bid in 2008 while under indictment for bribery, saw photos of the infamous frozen cash. It was wrapped in $10,000 increments and concealed in boxes of Pillsbury pie crust and Boca burgers. Photo by the U.S. Attorney’s Office.
Attorney General Sessions, waving the bloody shirt of the War on Drugs, nevertheless wants to continue civil asset forfeiture and expand it, if he can get away with it. His motivations are unimportant other than how they forecast all the draconian policies he’s likely to see through while he is in charge of the Department of Justice. The important thing is that he has opened up one of the very few issues that attracts a bipartisan consensus in Congress, and that has been for less civil asset forfeiture, not more.
Highway robbery in Stanley Kubrick’s 1975 film Barry Lyndon, with Ryan O’Neal as Redmond Barry. Under America’s civil asset forfeiture laws, the gold guineas in Barry’s purse, and the horse he rode in on, could be forfeited to the robbers, or police.
The strange history of this policy of official stealing from the innocent and the guilty alike also matters little, except perhaps to those appellate court judges who fall back on referring to obscure precedents of legal reasoning as convoluted and ultimately irrelevant as the debates of clerics who wondered how many angels might dance on the head of a pin. Congress can take this matter away from both Sessions and the judges by enacting legislation rolling it back. Really it should be swept away entirely, along with the War on Drugs it purportedly assists, as failed policies which have corrupted the police and eroded public trust every bit as much and in the same way as Prohibition did in the early decades of the twentieth century, when civil asset forfeiture first became a major police tactic. It seems we never learn lessons once and for all, but have to forever relearn them.
― Ed.